A structured project management process is vital for the successful completion of projects. It helps teams effectively manage projects, optimize resources, and align actions with clear project objectives. By utilizing a defined process, project teams can reduce risks and ensure that projects meet both timelines and deliverables, leading to a successful project outcome.
What is the project management process?
The project management body of knowledge defines the project lifecycle into five essential process groups: project initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closing. These phases guide the team to complete successful projects by ensuring clear workflows and milestones are followed from start to finish.
Popular project management methodologies
Different project management methodologies, such as Agile project management and Waterfall are discussed in the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) and provide structured approaches for managing project schedules, scope, and resources.
Agile focuses on flexibility and iterative development, while Waterfall follows a linear approach. The PMBOK provides project managers with the fundamental practices needed to achieve organizational results and excellence.
Phase 1: Project initiation
Project initiation is the first critical step where the project manager can outline the business case and high-level project scope. The project charter is created in this phase, detailing the project objectives, stakeholders, and initial risks. A solid project charter ensures clarity and alignment from the beginning, setting up the foundation for success.
Using visuals to communicate project goals
Tools like Snagit help visualize the project scope and project objectives, simplifying the communication of complex goals with stakeholders. These visuals make it easier to discuss and align on key project aspects during meetings.
The best snipping tool for Windows and Mac
Don’t let clumsy built-in tools hold you back. Take and edit screenshots with Snagit!
Get started for free
Phase 2: Project planning
A clearly defined project scope prevents scope creep, which can derail project progress by introducing unplanned tasks. A well-managed scope ensures that the project remains focused and that expectations are realistic.
Developing a detailed project plan
During project planning, the team creates a comprehensive project schedule, detailing timelines, milestones, and project deliverables. While having a clear schedule is essential to keeping the project on track, it’s important to avoid overloading it with too many rigid details.
Teams should focus on identifying the real hard constraints and dependencies while also recognizing areas where more flexibility is possible. Overly detailed schedules can lead to frustration if minor delays derail the entire timeline.
By distinguishing between non-negotiable deadlines and softer milestones, teams can adapt more efficiently as the project progresses. This approach encourages agility while still ensuring that the project’s overall direction remains clear.
Creating a risk management plan
An essential part of planning is crafting a risk management plan, identifying potential project risks, and creating strategies to mitigate them. Teams often use screen capture tools to create risk matrices or visual charts to communicate these risks to stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is aware of potential challenges with the project execution phase.
Phase 3: Project execution
The execution phase is where the project team brings the plan to life. All tasks and project deliverables are completed according to the project plan. It’s important to utilize collaboration tools and regularly check in with the team and stakeholders to ensure progress is on track and goals are being met.
Tracking and managing project progress with visuals
Tools like Snagit, a screen capture software, help capture and track project progress visually through charts or screenshots of dashboards, which can be shared with stakeholders. Using visuals makes tracking easier and allows for quicker updates, keeping everyone aligned.
Phase 4: Project monitoring and controlling
The monitoring and controlling phase runs alongside execution, with a focus on tracking project performance. The team uses key performance indicators (KPIs) to ensure the project is progressing according to the plan. This phase also involves addressing changes that may arise.
Handling changes and updates
Implementing a change control process ensures any adjustments to the project schedule, scope, or budget are properly handled. Visual tools can be used to document changes and update all stakeholders, ensuring transparency.
Phase 5: Project closing
During the closing phase, all project documents and project deliverables are finalized and handed over to the relevant parties. This is also when the team confirms that all objectives have been met and the project is officially closed.
Reviewing lessons learned
Reflecting on lessons learned during the project is a critical step for a team’s continuous improvement and helps the team improve their processes for future project success. While this is typically done as a post-project review to ensure that successes are celebrated and mistakes are avoided in the next initiative, teams should always be learning and reflecting back throughout the project lifecycle.
Stop repeat questions
Create clear videos and guides with Snagit so you only have to explain tasks once.
Get started for free
How agile project management fits into the process
Agile project management allows for an adaptive approach by breaking work into shorter time increments, often called sprints or iterations, while focusing on regular feedback and continuous improvement.
Agile is well-suited to projects that require flexibility and quick adjustments. It can fit into any of the five process phases, from project initiation to project closing. Different agile methodologies offer unique advantages. Scrum organizes work into sprints with daily check-ins to track progress, while Kanban visualizes workflows to limit tasks in progress and improve efficiency.
Extreme Programming (XP) emphasizes high-quality code through practices like pair programming and test-driven development. All share Agile’s focus on flexibility, collaboration, and iterative delivery. With all of that being said, each situation is unique, and these methodologies can be adapted and/or combined to meet the needs of the teams doing the work.
Using visuals to communicate in agile
Snagit and similar tools can help visualize sprint summaries and agile boards, providing clear snapshots of project progress during daily stand-ups or sprint reviews.
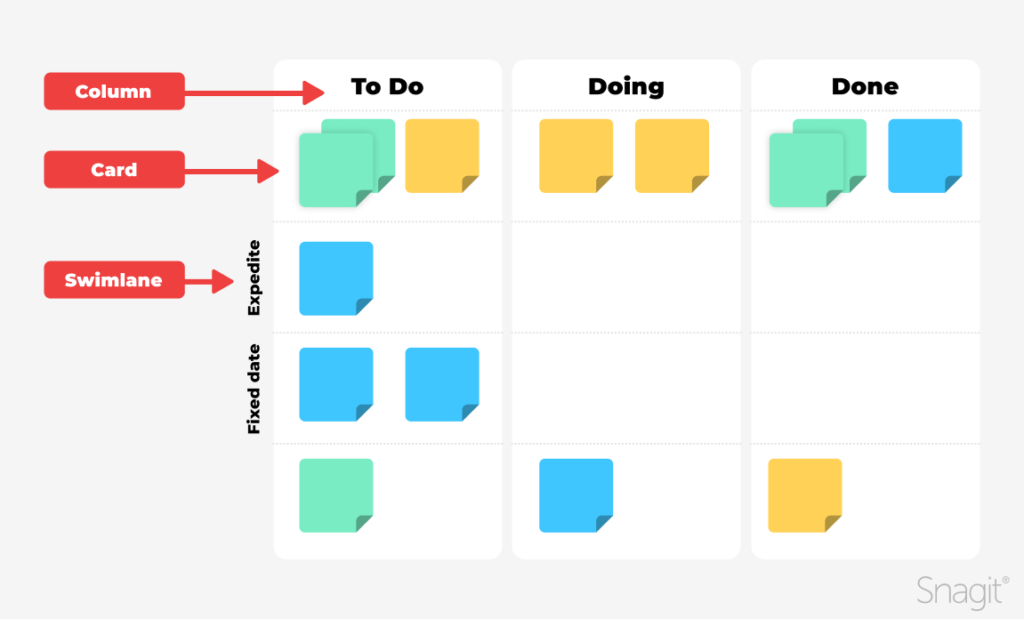
Best practices for a successful project management process
Clear communication between the project team and stakeholders is essential. Keeping everyone informed and aligned throughout the management process ensures smooth execution and minimal misunderstandings. Therefore, conducting regular demos and check-ins is an excellent way to achieve this.
Document everything
From the project charter to final reports, creating and maintaining accurate project documents is vital for tracking decisions and ensuring transparency. This documentation helps the team stay aligned and track project progress efficiently.
Use visual tools to simplify complex information
Visual tools like Snagit simplify communication by turning complex information into clear visuals. Visual aids such as charts, timelines, and screenshots can all help communicate critical information to stakeholders more effectively.
The key to managing successful projects
A well-structured project management process, encompassing the entire project life cycle and clearly defined phases, is the foundation of any successful project. A robust project management plan, supported by strong communication and the identification of relevant knowledge areas, ensures effective project work.
Using visual tools like Snagit can enhance communication, streamline project tracking, and lead to successful project outcomes. When combined with the right project management methodology, these practices help teams complete projects efficiently and with less risk.
Get started today with a free trial of Snagit screen capture and recording software.



Share